The Material Mechanics Laboratory is designed to characterize the mechanical properties of a variety of materials (such as biological and bio-artificial materials, rubber like materials, shape memory allows), using specialized testing equipment and standard testing methods.


Testing Equipments
The MTS Insight Testing Systems 10 kN (MTS System Corporation) is designed for medium-force testing applications. The MTS system performs standard tests such as peel, tear, shear, tensile, compression, and flex/bend. More advanced tests can also be performed, such as creep, stress relaxation, and multi-cycle. The MTS system consists of a double-column load frames and a moving solid steel cross head (Fig. 1a). The MTS system is equipped by wedge and pneumatic grips (Fig. 1b and Fig.1c) for testing hard and soft materials, respectively. A load-cell anchored to the cross-head detects the applied loads during testing. Two cells, respectively, of 10 kN and 250 N are supplied with the device (Fig. 1d and Fig.1e). The ME-46 Video Extensometer measures with accurate resolution the specimen deformations.
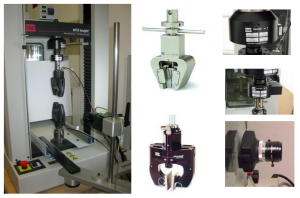
Fig. 1: (a) MTS Insight 10 kN testing device. (b) Wedge grip and (c) pneumatic grip. (d) Load cell of 10 kN and (e) load cell of 250 N. (f) Video extensometer.
TestWorks application software has the power to streamline testing procedures. A user-friendly interface with intuitive menus and controls make initial test definition, test execution, and report generation easy for both simple and complex testing (Fig. 1). The TestWorks software offers packages to run a variety of testing methods, including peel, tear, shear, tensile, compression, creep, stress, cyclic and strain.
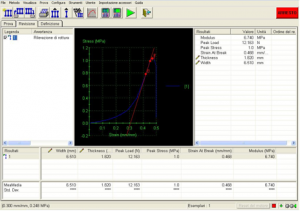
Fig. 1: Interface TestWorks4 software.
Standard testing methods
- Uniaxial Tensile Tests
- Peeling/Tear Tests
Current testing activities
- Testing of Soft Biological Materials
- Uniaxial Tests of Human Aorta
- Uniaxial Tests of Pig Aorta
- Uniaxial Tests of Mouse Aorta
- Peeling Tests of Pig Aorta
- Uniaxial Tests of ABS/Elastomer Materials
- Testing of Rubber Materials
- Testing of Nitinol wires
Main collaborations
- IRCCS San Matteo, Cardiochirurgia, Dott. A. Mazzola
- IRCCS San Matteo, Radiologia, Dott. R. Dore
Acknowledgements
The lab activities are kindly supported also by:
- European Research Council (ERC) through the ISOBIO project
- Cariplo Foundation through the project 2009-2822